Release 2020-11-23
- This version:
- http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology/1.5
- Latest version:
- http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology
- Revision:
- 1.5
- Authors:
- Miriam Landkammer, (University of Salzburg)
- Peter Hinkelmanns, (University of Salzburg)
- Manuel Schwembacher, (University of Salzburg)
- Katharina Zeppezauer-Wachauer, (University of Salzburg)
- Isabella Nicka, (University of Salzburg)
- Download serialization:
-
- Repository:
-
- Cite as:
- Landkammer, Miriam; Hinkelmanns, Peter; Schwembacher, Manuel; Zeppezauer-Wachauer, Katharina; Nicka, Isabella (2020): ONAMA. Ontology of Narratives of the Middle Ages. Version 1.5. University of Salzburg. Salzburg. DOI 10.5281/zenodo.4285987, updated on 2020-11-23.
- DOI:
Abstract
ONAMA – Ontology of Narratives of the Middle Ages enables the systematic comparison of the structures and building blocks of many narratives in medieval literature and images.
Introduction
This ontology provides a model for a cross-media description of actions, actors, settings and temporal structures. In addition to the constituting basic elements of transmedial narrative nuclei, these descriptions record the respective textual and pictorial realizations in detail. They thus go beyond the plot of a story or picture cycle. ONAMA allows to identify patterns and peculiarities in the construction of narratives, which can then be examined for their underlying causes and functions.
ONAMA enables to annotate image and text sources in a way that the generated data provide information about the emergence and transmission of narrative nuclei, figure constellations, patterns of actions, etc. in the respective medium and in cross-media synopses.
The ONAMA ontology was developed in the course of the project ONAMA - Ontology of Narratives of the Middle Ages, which is carried out as an interdisciplinary cooperation between the Middle High German Conceptual Database (MHDBDB) and the Institute for Medieval and Early Modern Material Culture (IMAREAL), both of which are affiliated to the Interdisciplinary Center for Medieval and Early Modern Studies (IZMF) at the University of Salzburg. The project is funded by the go!digital programme of the Austrian Academy of Sciences.
Namespace declarations
| onama | <http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#> |
| owl | <http://www.w3.org/2002/07/owl> |
| xsd | <http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema> |
| rdfs | <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema> |
| core | <http://www.w3.org/2004/02/skos/core> |
| rdf | <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns> |
| terms | <http://purl.org/dc/terms> |
| cidoc-crm | <http://www.cidoc-crm.org/cidoc-crm> |
| vann | <http://purl.org/vocab/vann> |
| foaf | <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1> |
| dc | <http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1> |
Overview
Purpose
ONAMA – Ontology of Narratives of the Middle Ages – allows for a systematic comparison of the structures and building blocks of narratives in literature and images. With the model, the narrative strategies of images and texts can be annotated, thus creating a basis for their subsequent analysis. Designed for the in-depth recording and publishing of medieval narratives on the Semantic Web, ONAMA can also be adapted to literary or pictorial narratives from other periods.
Model Overview
An ONAMA narrative is defined as a single activity, an event, a change of state. This core element of ONAMA is recorded either as an abstract, transmedial concept or as a realisation of a concept in a concrete text or visual work of art. Every narative is based on an action. Actors, objects, places and temporal entities are connected to narratives via hierarchically layered semantic roles. Semantic roles are a concept from linguistics; they suggest what function an entity has in a narrative. In addition, entities can be assigned general or temporary entity functions (such as hero, opponent, talisman). On the level of narrative realisations, chronological orders are specified. In contrast, narrative concepts are set into meronymic relations via properties broader and narrower. ONAMA imports several entities from the CIDOC Conceptual Reference Model. It provides properties to associate identifiers from Wikidata, GND and ICONCLASS to the individual entities created by the annotators.
This ontology has the following classes and properties:
Classes
- Actant Role
- Action
- Actor
- Agent Role
- Animal
- Benefactive Role
- Causer Role
- Co-Agent Role
- Collection
- Concept
- Entity Function
- Experiencer Role
- Goal Role
- Group
- Instrument Role
- Localisation Role
- Mode Role
- MythicalBeing
- Narrative
- Participator Role
- Patient Role
- Persistent Item
- Person
- Place
- Place Role
- Possessor Role
- Predicative Role
- Realisation
- Recipient Role
- Semantic Role
- Source Role
- Stimulus Role
- Temporal Entity
- Temporality Role
- Text Passage
- Textual Realisation
- Theme Role
- Thing
- Time Span
- Undergoer Role
- Verb
- Visual Realisation
- Witness Role
Object Properties
- broader
- broader transitive
- first in collection
- has action
- has actor
- has Entity Function
- has general entity function
- has narrative
- has place
- has semantic role
- has supplementary concept
- has temporal entity
- has temporary entity function
- has text passage
- has thing
- has verb
- is realised as supplementary narrative by
- is realised by
- is related to
- narrower
- narrower transitive
- next
- next fabula
- next syuzhet
- occurs simultaneously
- part of collection
- previous
- previous fabula
- previous syuzhet
- realises
- realises as supplementary narrative
Data Properties
Description
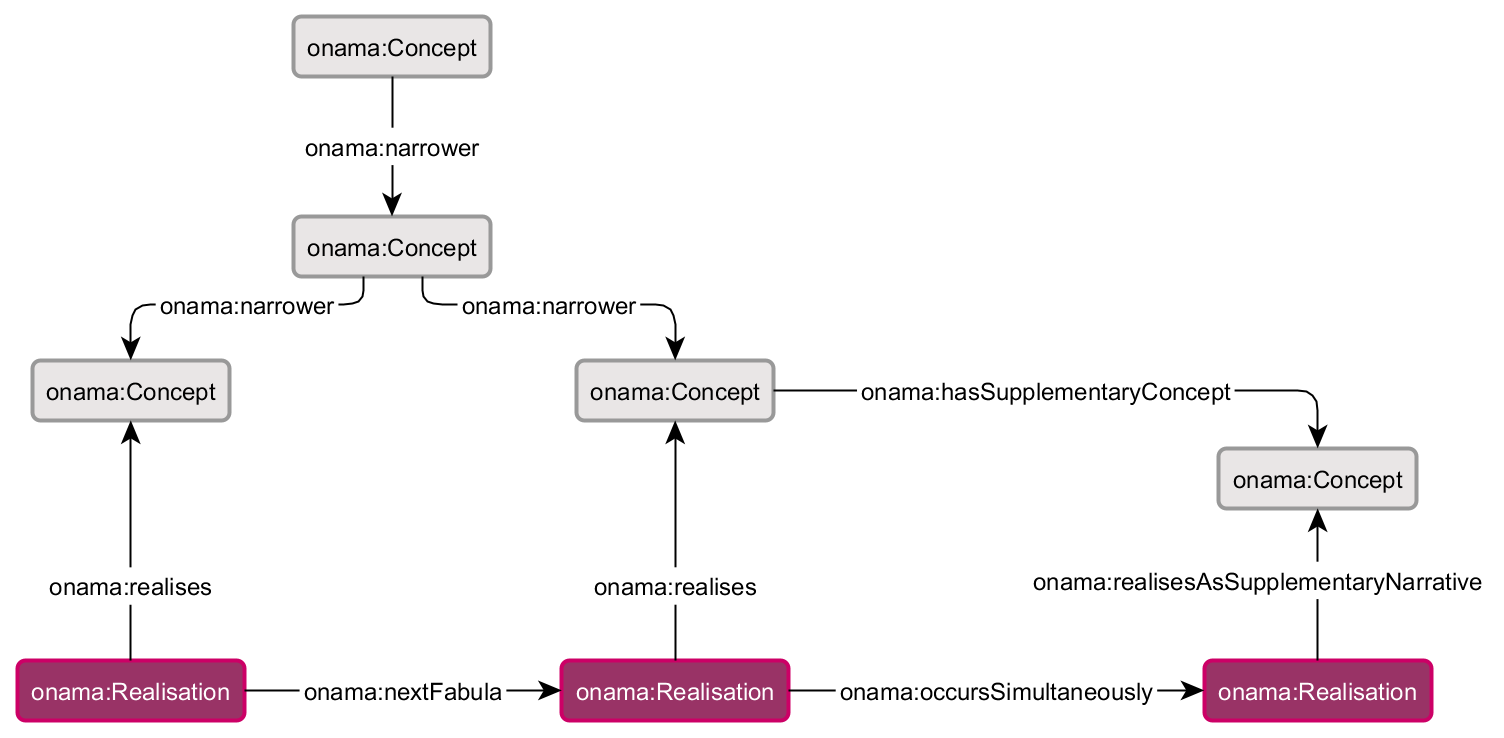
The diagram shows the meronymic relations between concepts as well as the chronological order which is indicated on the level of realisations. Especially in the recording of pictorial narratives, a means of weighting narratives must be introduced: subplots, for example additional scenes shown in the background of a picture, are indexed using the edges has supplementary concept and realises as supplementary narrative.
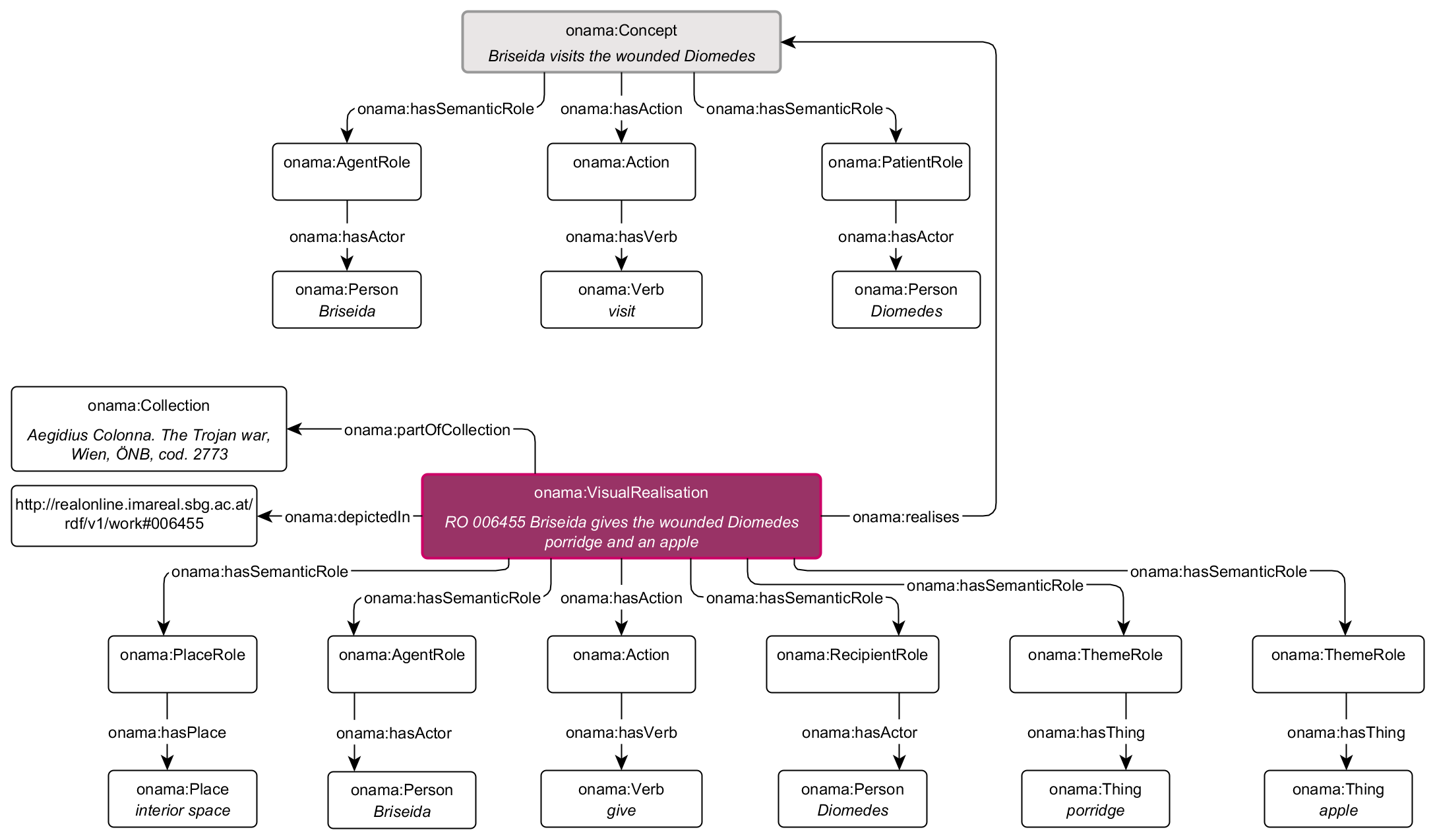
Using the example of a narrative from medieval adaptations of the Trojan war, the diagram shows how concepts and realisations are recorded with ONAMA. The visual realisation from Codex 2773 in the collection of the Österreichische Nationalbibliothek (Austrian National Library) is found in the database REALonline at number 006455.
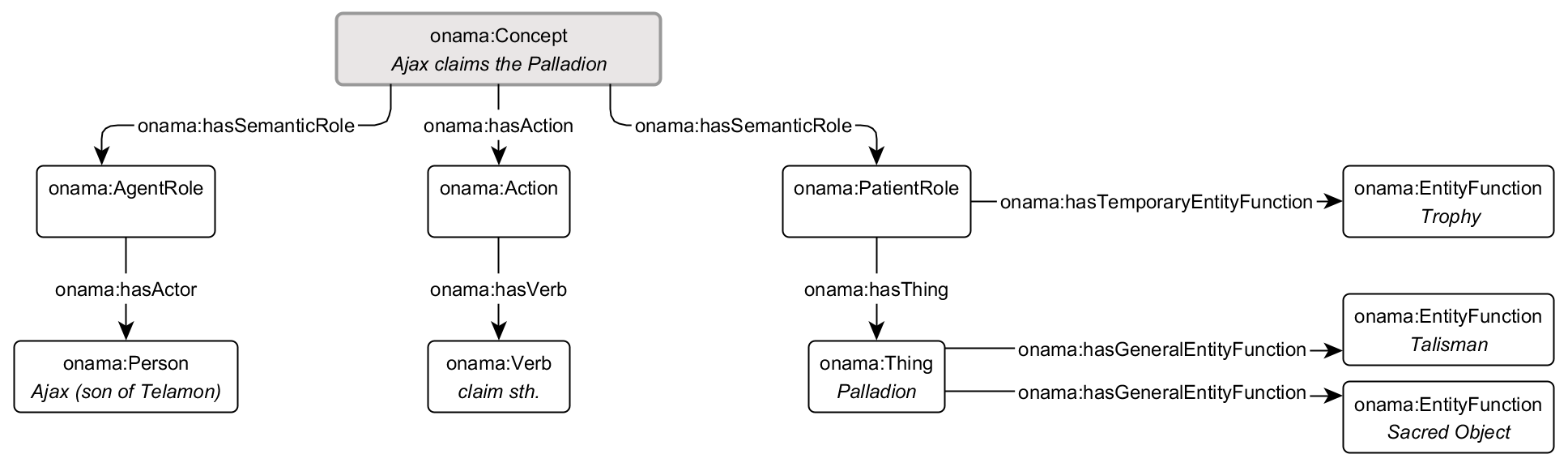
Actors or things can take on narrative functions that apply generally or only in a specific situation. Entity functions are therefore either directly attached to an actor/thing or to the semantic role node that lies between a narrative and an actor/thing taking part in the narrative.
Classes, properties and dataproperties
This section provides details for each class and property defined by Ontology of Narratives of the Middle Ages:
Classes
- Actant Role
- Action
- Actor
- Agent Role
- Animal
- Benefactive Role
- Causer Role
- Co-Agent Role
- Collection
- Concept
- Entity Function
- Experiencer Role
- Goal Role
- Group
- Instrument Role
- Localisation Role
- Mode Role
- MythicalBeing
- Narrative
- Participator Role
- Patient Role
- Persistent Item
- Person
- Place
- Place Role
- Possessor Role
- Predicative Role
- Realisation
- Recipient Role
- Semantic Role
- Source Role
- Stimulus Role
- Temporal Entity
- Temporality Role
- Text Passage
- Textual Realisation
- Theme Role
- Thing
- Time Span
- Undergoer Role
- Verb
- Visual Realisation
- Witness Role
Actant Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#ActantRole
Actants are elements that perform or are subjected to an action.
- has super-classes
- Semantic Role c
- has sub-classes
- Causer Role c, Participator Role c, Undergoer Role c
Actionc
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#Action
Abstract concepts of actions from the class "Verb" are created as a separate node for each Narrative, which belongs to the class "Action".
- has super-classes
- concept, e28 conceptual object
- is in domain of
- has REALonline scenary graph node dp, has verb op
- is in range of
- has action op
Actorc
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#Actor
The class "Actor" denotes protagonists who become active in a narrative and comprises persons, groups, animals and mythical beings.
- has super-classes
- Persistent Item c
- has sub-classes
- Animal c, Group c, MythicalBeing c, Person c
- is in range of
- has actor op
Agent Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#AgentRole
An Agent is the usually animated participant who deliberately causes the situation described by the verbal predicate.
"Traditionally, the Agent is characterized as the typically animated participant who deliberately brings about the situation described by the verbal predicate." (Primus, Beatrice. 2012. Semantische Rollen. Kurze Einführungen in die germanistische Linguistik 12. Heidelberg: 16-17 [Translation: ONAMA Project])
"An agent is usually the grammatical subject of the verb in an active clause. A prototypical agent is conscious, acts with volition (on purpose), and performs an action that has a physical, visible effect." (https://glossary.sil.org/term/agent-semantic-role 18.07.2019)
"Agent – The ‘doer’, or instigator of the action denoted by the predicate." (Aarts, Bas. 2001. English Syntax and Argumentation. 2nd ed. Modern linguistics series. Basingstoke: 94)
- has super-classes
- Causer Role c
Animalc
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#Animal
Refers to an animal as a protagonist of a Narrative.
- has super-classes
- Actor c
Benefactive Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#BenefactiveRole
Benefactive is the semantic role of a referent which is advantaged or disadvantaged by an event.
"A beneficiary is the semantic role of a referent which is advantaged or disadvantaged by an event." (https://glossary.sil.org/term/beneficiary-semantic-role 18.07.2019)
"Benefactive – The entity that benefits from the action or event denoted by the predicate." (Aarts, Bas. 2001. English Syntax and Argumentation. 2nd ed. Modern linguistics series. Basingstoke: 94)
- has super-classes
- Participator Role c
Causer Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#CauserRole
- has super-classes
- Actant Role c
- has sub-classes
- Agent Role c, Co-Agent Role c, Stimulus Role c
Co-Agent Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#Co-AgentRole
Denotes a Co- or Re-Agent in verbs that describe actions that are in the relation of action and reaction to each other.
"Co-Agent: [...] Co- or Re-Agent in verbs that describe actions that are in the relation of action and reaction to each other (meet someone, follow someone, obey someone, imitate someone, allow someone to do something, help someone." (Wegener, Heide. 1985. Der Dativ im heutigen Deutsch. Tübingen: 261, quoted in Primus, Beatrice. 2012. Semantische Rollen. Kurze Einführungen in die germanistische Linguistik 12. Heidelberg: 56 [Translation: ONAMA Project])
- has super-classes
- Causer Role c
Collectionc
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#Collection
Identifies the textual or pictorial context from which the Narrative originates.
- has super-classes
- e28 conceptual object
- is in domain of
- first in collection op, has MHDBDB sigil dp, has Mhdbdb Sigil URL dp
- is in range of
- part of collection op
Conceptc
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#Concept
A concept is the definition of a narrative as an abstraction without a concrete reference to a realisation. It can serve as a cross-linking instance between different realisations.
- has super-classes
- Narrative c
- is in domain of
- broader op, broader transitive op, has supplementary concept op, is realised as supplementary narrative by op, is realised by op, narrower op, narrower transitive op
- is in range of
- broader op, broader transitive op, has supplementary concept op, narrower op, narrower transitive op, realises op, realises as supplementary narrative op
- is disjoint with
- Realisation c
Entity Functionc
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#EntityFunction
Denotes a function of an Actor or Thing in a Narrative (for example hero, ruler, villain, trophy, talisman...).
- has super-classes
- concept, e28 conceptual object
- is in range of
- has Entity Function op, has general entity function op, has temporary entity function op
Experiencer Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#ExperiencerRole
An Experiencer is an animate entity that experiences a sensory perception or mental state designated by the predicate.
- has super-classes
- Participator Role c
Goal Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#GoalRole
Goal – The location or entity in the direction of which something moves.
"Goal is the semantic role of the: place to which something moves; thing toward which an action is directed." (https://glossary.sil.org/term/goal-semantic-role 18.07.19)
"Goal – The location or entity in the direction of which something moves." (Aarts, Bas. 2001. English Syntax and Argumentation. 2nd ed. Modern linguistics series. Basingstoke: 94)
- has super-classes
- Localisation Role c
Groupc
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#Group
Denotes a group of individuals who are involved in a Narrative.
"This class comprises any gatherings or organizations of two or more people that act collectively or in a similar way due to any form of unifying relationship. In the wider sense this class also comprises official positions which used to be regarded in certain contexts as one actor, independent of the current holder of the office, such as the president of a country." (http://www.cidoc-crm.org/html/5.0.4/cidoc-crm.html#E74 18.07.19)
- has super-classes
- Actor c
Instrument Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#InstrumentRole
Instrument – The medium by which the action or event denoted by the predicate is carried out.
Paris kills Achill with the arrow.
"The instrument is the semantic role for a normally inanimate entity which, together with a controlling causer (agent), causes the situation described by the predicate or its result." (Primus, Beatrice. 2012. Semantische Rollen. Kurze Einführungen in die germanistische Linguistik 12. Heidelberg: 72)
"Instrumental – means or tools (with what?, by what?)." (Eisenberg, Peter, Jörg Peters, Peter Gallmann, Cathrine Fabricius-Hansen, Damaris Nübling, Irmhild Bartz, Thomas A. Fritz, and Reinhard Fiehler. 2009. Die Grammatik: Unentbehrlich für richtiges Deutsch. 8. Aufl. Der Duden in zwölf Bänden 4. Mannheim, Zürich: 784 [Translation: ONAMA Project])
"Instrument – The medium by which the action or event denoted by the predicate is carried out." (Aarts, Bas. 2001. English Syntax and Argumentation. 2nd ed. Modern linguistics series. Basingstoke: 95)
- has super-classes
- Semantic Role c
Localisation Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#LocalisationRole
Local Adverbial; Adverbial of Place.
Local Adverbial: place (where?) – direction, way, destination (where?) – origin (where from?) – spatial extent (how far?). (cf. Eisenberg, Peter, Jörg Peters, Peter Gallmann, Cathrine Fabricius-Hansen, Damaris Nübling, Irmhild Bartz, Thomas A. Fritz, and Reinhard Fiehler. 2009. Die Grammatik: Unentbehrlich für richtiges Deutsch. 8. Aufl. Der Duden in zwölf Bänden 4. Mannheim, Zürich: 783 [Translation: ONAMA Project])
- has super-classes
- Semantic Role c
- has sub-classes
- Goal Role c, Place Role c, Source Role c
Mode Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#ModeRole
Modal Adverbial; Adverbial of manner
Modal Adverbial: procedure (how?) – degree, measure, intensity (how much?) – material quality (from what?). (cf. Eisenberg, Peter, Jörg Peters, Peter Gallmann, Cathrine Fabricius-Hansen, Damaris Nübling, Irmhild Bartz, Thomas A. Fritz, and Reinhard Fiehler. 2009. Die Grammatik: Unentbehrlich für richtiges Deutsch. 8. Aufl. Der Duden in zwölf Bänden 4. Mannheim, Zürich: 784 [Translation: ONAMA Project])
- has super-classes
- Semantic Role c
MythicalBeingc
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#MythicalBeing
Denotes a mythical being or a deity that is involved in a Narrative.
- has super-classes
- Actor c
Narrativec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#Narrative
A Narrative is an activity, an event, a change of state. Every Narrative is based on an Action. The Verb specifies which semantic roles are filled by Actors, Things, Places and Temporal Entities. Narratives are usually linked to other Narratives and are themselves part of a larger Narrative.
"For me, as soon as there is even a single action or event, there is a story, because then there is already a change, a transition from before to after." (Genette, Gerard. 2010. Die Erzählung. Übersetzt von Andreas Knop. 3. Aufl. Paderborn: 183 [Translation: ONAMA Project])
"one will define narrative […] as the representation of an event or sequence of events" (Genette, Gerard. 1987. Narrative Discourse. An Essay in Method. Translated by Jane E. Lewin. 4th. ed. Ithaca, NY: 127)
- has super-classes
- concept, e28 conceptual object
- has sub-classes
- Concept c, Realisation c
- is in domain of
- has action op, has semantic role op
- is in range of
- has narrative op
- is disjoint with
- Semantic Role c
Participator Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#ParticipatorRole
The class includes typically animate entities which participate in the event but have no control or initiative associated it.
Cf. on the hierarchy of semantic roles: (Eisenberg, Peter, Jörg Peters, Peter Gallmann, Cathrine Fabricius-Hansen, Damaris Nübling, Irmhild Bartz, Thomas A. Fritz, and Reinhard Fiehler. 2009. Die Grammatik: Unentbehrlich für richtiges Deutsch. 8. Aufl. Der Duden in zwölf Bänden 4. Mannheim, Zürich: 391).
- has super-classes
- Actant Role c
- has sub-classes
- Benefactive Role c, Experiencer Role c, Possessor Role c, Recipient Role c, Witness Role c
Patient Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#PatientRole
Patient – The living entity affected by an event or action and not exercising control over the event; the object or matter affected.
"Patient is the semantic role of a participant who is physically manifestly affected in the event described by the predicate and whose state changes physically. The basic concepts that characterize a patient are therefore physical affectedness (also known as affectation) and change of state." (Primus, Beatrice. 2012. Semantische Rollen. Kurze Einführungen in die germanistische Linguistik 12. Heidelberg: 31-32 [Translation: ONAMA Project])
"Group 3: Patient (affected object or person who does not exercise control over the event/action); matter affected." (Eisenberg, Peter, Jörg Peters, Peter Gallmann, Cathrine Fabricius-Hansen, Damaris Nübling, Irmhild Bartz, Thomas A. Fritz, and Reinhard Fiehler. 2009. Die Grammatik: Unentbehrlich für richtiges Deutsch. 8. Aufl. Der Duden in zwölf Bänden 4. Mannheim, Zürich: 391 [Translation: ONAMA Project])
"Patient – The ‘undergoer’ of the action or event denoted by the predicate." (Aarts, Bas. 2001. English Syntax and Argumentation. 2nd ed. Modern linguistics series. Basingstoke: 94)
- has super-classes
- Undergoer Role c
Persistent Itemc
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#PersistentItem
This class includes living beings, objects and intellectual products which have a persistent identity.
"Persistent items have a persistent identity. They are sometimes known as 'endurants' in philosophy. They can be repeatedly recognized within the duration of their existence by identity criteria rather than by continuity or observation. Persistent Items can be either physical entities, such as people, animals or things, or conceptual entities such as ideas, concepts, products of the imagination or common names." (http://www.cidoc-crm.org/html/5.0.4/cidoc-crm.html#E77 18.07.19)
- has sub-classes
- Actor c, Thing c
- is in domain of
- has general entity function op
- is disjoint with
- Place c, Semantic Role c, Time Span c, Place c, Temporal Entity c, Time Span c
Personc
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#Person
Denotes a person who is involved in a Narrative.
"This class comprises real persons who live or are assumed to have lived. Legendary figures that may have existed, such as Ulysses and King Arthur, fall into this class." (http://www.cidoc-crm.org/html/5.0.4/cidoc-crm.html#E21 18.07.19)
- has super-classes
- Actor c
Placec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#Place
Describes extensions in space that are usually immobile (for example castle, garden, valley...).
- is in range of
- has place op
- is disjoint with
- Persistent Item c, Time Span c, Persistent Item c, Temporal Entity c, Time Span c
Place Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#PlaceRole
Locative – The specification of the place where the action or event denoted by the predicate is situated.
"Locative – The specification of the place where the action or event denoted by the predicate is situated." (Aarts, Bas. 2001. English Syntax and Argumentation. 2nd ed. Modern linguistics series. Basingstoke: 95)
- has super-classes
- Localisation Role c
Possessor Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#PossessorRole
Possessor is the semantic role of an entity that possesses something.
- has super-classes
- Participator Role c
Predicative Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#PredicativeRole
Like the predicate, the predicative makes a statement about one or more other phrases. A predicative never has a finite verb as its core, at most an adjectivally used participle. A predicative can be an addition to a verb that is largely empty of content. The copula verbs are to be, to become, and to remain.
The princes elect Frederick as king. – "as king": predicative.
(cf. Eisenberg, Peter, Jörg Peters, Peter Gallmann, Cathrine Fabricius-Hansen, Damaris Nübling, Irmhild Bartz, Thomas A. Fritz, and Reinhard Fiehler. 2009. Die Grammatik: Unentbehrlich für richtiges Deutsch. 8. Aufl. Der Duden in zwölf Bänden 4. Mannheim, Zürich:787–788 [Translation: ONAMA Project])
- has super-classes
- Semantic Role c
Realisationc
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#Realisation
Realisations are concrete implementations of narrative Concepts in a specific medium, such as a text or an image.
- has super-classes
- Narrative c
- has sub-classes
- Textual Realisation c, Visual Realisation c
- is in domain of
- next op, next fabula op, next syuzhet op, occurs simultaneously op, part of collection op, previous op, previous fabula op, previous syuzhet op, realises op, realises as supplementary narrative op
- is in range of
- first in collection op, is realised as supplementary narrative by op, is realised by op, next op, next fabula op, next syuzhet op, occurs simultaneously op, previous op, previous fabula op, previous syuzhet op
- is disjoint with
- Concept c
Recipient Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#RecipientRole
The recipient of an entity or information in verbs that denote the transfer of an object of possession or information.
"The recipient in the narrower sense is the recipient of an entity or information in verbs that denote the transfer of an object of possession or information." (Primus, Beatrice. 2012. Semantische Rollen. Kurze Einführungen in die germanistische Linguistik 12. Heidelberg: 44 [Translation: ONAMA Project])
- has super-classes
- Participator Role c
Semantic Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#SemanticRole
Contains the information of a Semantic Role associated with the Narrative.
- has super-classes
- concept, e28 conceptual object
- has sub-classes
- Actant Role c, Instrument Role c, Localisation Role c, Mode Role c, Predicative Role c, Temporality Role c
- is in domain of
- has REALonline scenary graph node dp, has actor op, has narrative op, has place op, has temporal entity op, has temporary entity function op, has thing op
- is in range of
- has semantic role op
- is disjoint with
- Narrative c, Persistent Item c
Source Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#SourceRole
Source – The location or entity from which something moves.
"Source – The location or entity from which something moves." (Aarts, Bas. 2001. English Syntax and Argumentation. 2nd ed. Modern linguistics series. Basingstoke: 95)
- has super-classes
- Localisation Role c
Stimulus Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#StimulusRole
A stimulus is the often inanimate trigger that causes the situation described by the verbal predicate. In combination with the Experiencer Role, Stimulus refers to the source or the object of a mental state.
"[T]he object of a mental state [...]. Every object of a mental state presupposes a state carrier (Experiencer)." (Primus, Beatrice. 2012. Semantische Rollen. Kurze Einführungen in die germanistische Linguistik 12. Heidelberg, 39 [Translation: ONAMA Project])
- has super-classes
- Causer Role c
Temporal Entityc
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#TemporalEntity
This class comprises all phenomena, such as periods, events and states, which happen over a limited extent in time; it is disjoint from Persistent Item.
"This class comprises all phenomena, such as the instances of E4 Periods, E5 Events and states, which happen over a limited extent in time.In some contexts, these are also called perdurants. This class is disjoint from E77 Persistent Item." (http://www.cidoc-crm.org/html/5.0.4/cidoc-crm.html#E2 18.07.19)
- is in range of
- has temporal entity op
- is disjoint with
- Persistent Item c, Place c, Time Span c
Temporality Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#TemporalityRole
Indicates the period or time of an event.
"Specifies a period in time, point in time, or the like, that an action or an event covers. Temporal adverbial; adverbial of time." (Eisenberg, Peter, Jörg Peters, Peter Gallmann, Cathrine Fabricius-Hansen, Damaris Nübling, Irmhild Bartz, Thomas A. Fritz, and Reinhard Fiehler. 2009. Die Grammatik: Unentbehrlich für richtiges Deutsch. 8. Aufl. Der Duden in zwölf Bänden 4. Mannheim, Zürich: 784 [Translation: ONAMA Project]).
- has super-classes
- Semantic Role c
Text Passagec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#TextPassage
Denotes a section from a text; for instance in the Middle High German Conceptual Database (MHDBDB).
- has super-classes
- e54 dimension
- is in domain of
- from token dp, to token dp
- is in range of
- has text passage op
Textual Realisationc
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#TextualRealisation
Denotes the concrete implementation of a Concept in a text.
- has super-classes
- Realisation c
- is in domain of
- has text passage op
- is disjoint with
- Visual Realisation c
Theme Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#ThemeRole
Theme – The entity that is spatially moved or whose spatial position is indicated by the event (or state) designated in the predicate.
Jason brings the Golden Fleece (Theme) to Jolcos, Saint John (Theme) is on the island of Patmos, Saint Anthony (Theme) lives in the desert.
"Theme – The entity that is moved by the action or event denoted by the predicate." (Aarts, Bas. 2001. English Syntax and Argumentation. 2nd ed. Modern linguistics series. Basingstoke: 94).
In phrases with relocation verbs and position verbs: the entity whose spatial position is indicated. (cf. Primus, Beatrice. 2012. Semantische Rollen. Kurze Einführungen in die germanistische Linguistik 12. Heidelberg: 63-72, there under the term Lokatum [Translation: ONAMA Project])
- has super-classes
- Undergoer Role c
Thingc
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#Thing
This class comprises intellectual products or physical things.
"This general class comprises usable discrete, identifiable, instances documented as single units. They can be either intellectual products or physical things, and are characterized by relative stability. They may for instance either have a solid physical form, an electronic encoding, or they may be logical concept or structure." (http://www.cidoc-crm.org/html/5.0.4/cidoc-crm.html#E70 18.07.19)
- has super-classes
- Persistent Item c
- is in range of
- has thing op
Time Spanc
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#TimeSpan
This class comprises abstract temporal extents having a beginning, an end and a duration.
"This class comprises abstract temporal extents, in the sense of Galilean physics, having a beginning, an end and a duration. Time Span has no other semantic connotations. Time-Spans are used to define the temporal extent of instances of E4 Period, E5 Event and any other phenomena valid for a certain time. An E52 Time-Span may be identified by one or more instances of E49 Time Appellation. Since our knowledge of history is imperfect, instances of E52 Time-Span can best be considered as approximations of the actual Time-Spans of temporal entities. The properties of E52 Time-Span are intended to allow these approximations to be expressed precisely. An extreme case of approximation, might, for example, define an E52 Time-Span having unknown beginning, end and duration. Used as a common E52 Time-Span for two events, it would nevertheless define them as being simultaneous, even if nothing else was known." (http://www.cidoc-crm.org/cidoc-crm/E52_Time-Span 18.07.19)
- is disjoint with
- Persistent Item c, Place c, Persistent Item c, Place c, Temporal Entity c
Undergoer Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#UndergoerRole
Die von der im Prädikat benannten Handlung "betroffene" Entität.
Vgl. zur Hierarchie der semantischen Rollen: (Eisenberg, Peter, Jörg Peters, Peter Gallmann, Cathrine Fabricius-Hansen, Damaris Nübling, Irmhild Bartz, Thomas A. Fritz, and Reinhard Fiehler. 2009. Die Grammatik: Unentbehrlich für richtiges Deutsch. 8. Aufl. Der Duden in zwölf Bänden 4. Mannheim, Zürich: 391).
- has super-classes
- Actant Role c
- has sub-classes
- Patient Role c, Theme Role c
Verbc
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#Verb
The class "Verb" includes actions that allow the assignment of Semantic Roles.
- has super-classes
- concept, e28 conceptual object
- is in range of
- has verb op
Visual Realisationc
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#VisualRealisation
Refers to the concrete implementation of a Concept in an image.
- has super-classes
- Realisation c
- is in domain of
- depicted in dp, has Realonline Work URL dp
- is disjoint with
- Textual Realisation c
Witness Rolec
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#WitnessRole
Witness – The animate entity that witnesses the action or event denoted by the predicate.
- has super-classes
- Participator Role c
Object Properties
- broader
- broader transitive
- first in collection
- has action
- has actor
- has Entity Function
- has general entity function
- has GND equivalent
- has IconClass equivalent
- has narrative
- has place
- has related IconClass entry
- has related WikiData entry
- has semantic role
- has supplementary concept
- has temporal entity
- has temporary entity function
- has text passage
- has thing
- has verb
- has WikiData equivalent
- is realised as supplementary narrative by
- is realised by
- is related to
- narrower
- narrower transitive
- next
- next fabula
- next syuzhet
- occurs simultaneously
- part of collection
- previous
- previous fabula
- previous syuzhet
- realises
- realises as supplementary narrative
broaderop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#broader
The property "broader" relates a narrative Concept to the immediately superordinate Concept, indicating that a narrative is part of another narrative.
- has super-properties
- broader transitive op
- has domain
- Concept c
- has range
- Concept c
- is inverse of
- narrower op
broader transitiveop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#broaderTransitive
This property relates a narrative Concept to all the hierarchically superordinated narrative Concepts.
has characteristics: transitive
- has super-properties
- is related to op
- has sub-properties
- broader op
- has domain
- Concept c
- has range
- Concept c
- is inverse of
- narrower transitive op
first in collectionop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#firstInCollection
This property relates a Collection with the first Narrative (Realisation) in the Collection.
- has super-properties
- top object property
- has domain
- Collection c
- has range
- Realisation c
has actionop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasAction
This property relates a Narrative to the Action taking place in the Narrative.
has actorop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasActor
This property relates a Semantic Role to the Actor who holds this role.
- has super-properties
- top object property
- has domain
- Semantic Role c
- has range
- Actor c
has Entity Functionop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasEntityFunction
This property relates an Actor or a Thing to an Entity Function. Please use one of the two subproperties.
- has super-properties
- top object property
- has sub-properties
- has general entity function op, has temporary entity function op
- has range
- Entity Function c
has general entity functionop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasGeneralEntityFunction
This property relates an Actor or a Thing to a generally applicable Entity Function.
- has super-properties
- has Entity Function op
- has domain
- Persistent Item c
- has range
- Entity Function c
has GND equivalentop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasGNDEquivalent
This property/entity has a GND equivalent.
- has super-properties
- same as op
has IconClass equivalentop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasIconClassEquivalent
This property relates an entity with its IconClass equivalent.
- has super-properties
- same as op
has narrativeop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasNarrative
This property relates a Semantic Role to a Narrative.
- has super-properties
- top object property
- has domain
- Semantic Role c
- has range
- Narrative c
has placeop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasPlace
This property connects a Semantic Role, usually of the "localisation" type, with a place indication.
- has super-properties
- top object property
- has domain
- Semantic Role c
- has range
- Place c
has related IconClass entryop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasRelatedIconClassEntry
- has super-properties
- close match dp
- has domain
- Narrative c or Persistent Item c
- is also defined as
- data property
has related WikiData entryop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasRelatedWikiDataEntry
- has super-properties
- close match dp
- is also defined as
- data property
has semantic roleop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasSemanticRole
Basic relation between a narrative and its particular components.
- has super-properties
- top object property
- has domain
- Narrative c
- has range
- Semantic Role c
has supplementary conceptop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasSupplementaryConcept
This property relates a narrative Concept to a supplementary narrative Concept. A supplementary Concept is a Narrative, which is presented in addition to the respective "main action".
- has super-properties
- is related to op
- has domain
- Concept c
- has range
- Concept c
has temporal entityop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasTemporalEntity
This property relates a Semantic Role to a Temporal Entity that holds this role.
- has super-properties
- top object property
- has domain
- Semantic Role c
- has range
- Temporal Entity c
has temporary entity functionop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasTemporaryEntityFunction
This property relates a node of type "Semantic Role" to an Entity Function. The function thus applies temporarily – for the Narrative – to the Actor or Thing that holds the role.
- has super-properties
- has Entity Function op
- has domain
- Semantic Role c
- has range
- Entity Function c
has text passageop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasTextPassage
This property relates a Narrative realised in a text to the specific section of text that describes the Narrative in the MHDBDB.
- has super-properties
- top object property
- has domain
- Textual Realisation c
- has range
- Text Passage c
has thingop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasThing
This property relates a semantic role to an intellectual product or physical thing that holds this role.
- has super-properties
- top object property
- has domain
- Semantic Role c
- has range
- Thing c
has verbop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasVerb
This property relates an Action with the corresponding Verb.
has WikiData equivalentop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasWikiDataEquivalent
This property relates an entity with its WikiData equivalent.
- has super-properties
- same as op
is realised as supplementary narrative byop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#isRealisedAsSupplementaryNarrativeBy
This property relates those Concepts that are supplementary to a "main plot" to their Realisations.
Supplementary Concepts, which are presented in addition to the respective "main action", are connected with their Realisations via the properties "is realised as supplementary narrative by" and inversely "realises as supplementary narrative".
- has super-properties
- is realised by op
- has domain
- Concept c
- has range
- Realisation c
- is inverse of
- realises as supplementary narrative op
is realised byop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#isRealisedBy
The Narrative is realized through a specific work of literature or the visual arts; the property "is realised by" relates the Concept of a Narrative to its Realisation.
- has super-properties
- top object property
- has sub-properties
- is realised as supplementary narrative by op
- has domain
- Concept c
- has range
- Realisation c
- is inverse of
- realises op
is related toop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#isRelatedTo
The basic property to state a relation between two Narratives.
- has super-properties
- top object property
- has sub-properties
- broader transitive op, has supplementary concept op, narrower transitive op, next op, occurs simultaneously op, previous op
narrowerop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#narrower
This property relates one narrative Concept to another narrative Concept that can be considered part of the first.
This property is equivalent to skos:narrowMatch, which is used to indicate a hierarchical mapping connection between two Concepts. (https://www.w3.org/TR/2009/REC-skos-reference-20090818/#mapping 18.07.19)
- has super-properties
- narrower transitive op
- has domain
- Concept c
- has range
- Concept c
- is inverse of
- broader op
narrower transitiveop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#narrowerTransitive
This property points from one narrative Concept to all subordinate narrative Concepts.
has characteristics: transitive
- has super-properties
- is related to op
- has sub-properties
- narrower op
- has domain
- Concept c
- has range
- Concept c
- is inverse of
- broader transitive op
nextop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#next
On the level of Realisation, this property points from one Narrative to the next Narrative.
- has super-properties
- is related to op
- has sub-properties
- next fabula op, next syuzhet op
- has domain
- Realisation c
- has range
- Realisation c
- is inverse of
- previous op
next fabulaop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#nextFabula
On the level of Realisation, this property points from one Narrative to the next Narrative on the fabula path.
- has super-properties
- next op
- has domain
- Realisation c
- has range
- Realisation c
- is inverse of
- previous fabula op
next syuzhetop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#nextSyuzhet
On the level of Realisation, this property points from one Narrative to the next Narrative on the syuzhet path.
- has super-properties
- next op
- has domain
- Realisation c
- has range
- Realisation c
- is inverse of
- previous syuzhet op
occurs simultaneouslyop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#occursSimultaneously
On the level of Realisation, this property relates one Narrative to another Narrative that takes place simultaneously.
- has super-properties
- is related to op
- has domain
- Realisation c
- has range
- Realisation c
part of collectionop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#partOfCollection
This property points from a narrative Realisation to the Collection from which the Narrative originates.
- has super-properties
- top object property
- has domain
- Realisation c
- has range
- Collection c
previousop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#previous
On the level of realisation, this property points from one Narrative to the previous Narrative.
- has super-properties
- is related to op
- has sub-properties
- previous fabula op, previous syuzhet op
- has domain
- Realisation c
- has range
- Realisation c
- is inverse of
- next op
previous fabulaop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#previousFabula
On the level of realisation, this property points from one Narrative to the previous Narrative on the fabula path.
- has super-properties
- previous op
- has domain
- Realisation c
- has range
- Realisation c
- is inverse of
- next fabula op
previous syuzhetop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#previousSyuzhet
On the level of Realisation, this property points from one Narrative to the prevoious Narrative on the syuzhet path.
- has super-properties
- previous op
- has domain
- Realisation c
- has range
- Realisation c
- is inverse of
- next syuzhet op
realisesop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#realises
This property relates the Realisation of a Narrative with the Concept of that narrative.
- has super-properties
- top object property
- has sub-properties
- realises as supplementary narrative op
- has domain
- Realisation c
- has range
- Concept c
- is inverse of
- is realised by op
realises as supplementary narrativeop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#realisesAsSupplementaryNarrative
This property relates narrative Realisations that are supplementary to a "main plot" to their respective Concepts.
Supplementary Concepts, which are presented in addition to the respective "main action", are connected with their Realisations via the properties "is realised as supplementary narrative by" and inversely "realises as supplementary narrative".
- has super-properties
- realises op
- has domain
- Realisation c
- has range
- Concept c
- is inverse of
- is realised as supplementary narrative by op
Data Properties
- close match
- depicted in
- from token
- has MHDBDB sigil
- has Mhdbdb Sigil URL
- has REALonline scenary graph node
- has Realonline Work URL
- has related IconClass entry
- has related WikiData entry
- has Url
- to token
close matchdp
IRI: http://www.w3.org/2004/02/skos/core#closeMatch
- has super-properties
- top data property
- has sub-properties
- has related IconClass entry op, has related WikiData entry op
depicted indp
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#depictedIn
This property relates a Visual Realisation to the image object on which it is displayed, e.g. in REALonline.
- has super-properties
- top data property
- has domain
- Visual Realisation c
- has range
- any u r i
from tokendp
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#fromToken
This property points from a Text Passage to the first token of this group.
- has super-properties
- top data property
- has domain
- Text Passage c
- has range
- string
has MHDBDB sigildp
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasSigil
This property relates a Collection to a sigil in the MHDBDB.
- has super-properties
- top data property
- has domain
- Collection c
- has range
- string
has Mhdbdb Sigil URLdp
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasMhdbdbSigilURL
Reference to the URL of a MHDBDB sigil.
- has super-properties
- has Url dp
- has domain
- Collection c
- has range
- any u r i
has REALonline scenary graph nodedp
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasSceneNode
Reference to a node of a REALonline scene graph.
- has super-properties
- top data property
- has domain
- Action c
- Semantic Role c
- has range
- any u r i
has Realonline Work URLdp
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasRoWorkURL
Reference to a REALonline work URL.
- has super-properties
- has Url dp
- has domain
- Visual Realisation c
- has range
- any u r i
has related IconClass entryop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasRelatedIconClassEntry
- has range
- any u r i
- is also defined as
- object property
has related WikiData entryop
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasRelatedWikiDataEntry
- has range
- any u r i
- is also defined as
- object property
has Urldp
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#hasUrl
Reference to an URL.
- has super-properties
- top data property
- has sub-properties
- has Mhdbdb Sigil URL dp, has Realonline Work URL dp
to tokendp
IRI: http://onama.sbg.ac.at/ontology#toToken
This property points from a Text Passage to the last token of this group.
- has super-properties
- top data property
- has domain
- Text Passage c
- has range
- string
Legend
op: Object Properties
dp: Data Properties
ni: Named Individuals
References
- Hinkelmanns, Peter; Landkammer, Miriam; Nicka, Isabella; Schwembacher, Manuel; Zeppezauer-Wachauer, Katharina (2020): Erzählerische Spielräume. Medienübergreifende Erforschung von Narrativen im Mittelalter mit ONAMA. In Christof Schöch, Digital Humanities im deutschsprachigen Raum (Eds.): DHd 2020 Spielräume. Digital Humanities zwischen Modellierung und Interpretation. Jahrestagung des Verbands Digital Humanities im deutschsprachigen Raum. Konferenzabstracts. Universität Paderborn, 02.03.2020-06.03.2020. Paderborn: Zenodo; Universität Paderborn, pp. 131–135. Available online at https://zenodo.org/record/3666690#.X3Hme2gzat-.
- Hinkelmanns, Peter; Schwembacher, Manuel (2020): ONAMA. Ontology Of Narratives Of The Middle Ages. dha go!es digital Day 2020. [Online], 9/25/2020. Available online at https://zenodo.org/record/4048035#.X3HqXmgzat8.
- Hinkelmanns, Peter; Landkammer, Miriam; Nicka, Isabella; Schwembacher, Manuel; Zeppezauer-Wachauer, Katharina (in press): Beyond the Plot. Der Vergleich mittelalterlicher Narrative im Semantic Web mit ONAMA. In Vienna Doctoral Academy „Medieval Academy“ (Ed.): Narrare – producere – ordinare. New Approaches to the Middle Ages. Wien (Vienna Philological and Cultural Studies, 1).
- Hinkelmanns, Peter; Landkammer, Miriam; Nicka, Isabella; Schwembacher, Manuel; Zeppezauer-Wachauer, Katharina (2021 [in preparation]): Needful Things. Die Relationen der Dinge in einer Ontologie mittelalterlicher Narrative. In MEMO - Medieval and Early Modern Material Culture Online (7). Available online at https://memo.imareal.sbg.ac.at/.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Silvio Peroni for developing LODE, a Live OWL Documentation Environment, which is used for representing the Cross Referencing Section of this document and Daniel Garijo for developing Widoco, the program used to create the template used in this documentation.



This property is equivalent to skos:broadMatch, which is used to specify a hierarchical mapping connection between two concepts. (https://www.w3.org/TR/2009/REC-skos-reference-20090818/#mapping 18.07.19).